Credit management is a crucial aspect of running a successful business. It involves managing the credit risk of your customers, ensuring that they pay on time and in full, and minimizing the losses from bad debts. Credit management can also help you improve your cash flow, increase your profitability, and enhance your customer relationships.
However, credit management isn’t an easy task. Moreover, credit management is constantly evolving due to changing customer expectations, market conditions, and technological innovations.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what credit management is, how it differs from collections, what are its benefits, what are its main components, and what are the future trends that will shape the credit management industry, including AI, big data, and predictive analytics.
What Is Credit Management?
Credit management is managing your customers’ credit risk. How?
- Evaluating their financial situation
- Setting payment terms and conditions
- Extending credit limits
- Monitoring their payment behavior
- Taking action to recover overdue payments
Credit management aims to balance the trade-off between maximizing sales revenue and minimizing credit losses. It also seeks to maintain a healthy relationship with customers by providing them with flexible and convenient payment options.
Credit Management Vs. A/R Management Vs. Collections
Credit management is often confused with two related yet distinct business terms: Accounts receivable or A/R management and collections.
Credit management involves managing your client’s debt before, during, and after they’re awarded credit. Collections and AR management, on the other hand, are two different aspects of the process of receiving payments from customers who have already been granted credit.
Collections refer to the actions taken to recover the money from customers who haven’t paid their invoices on time or at all. AR management refers to the strategies and policies that aim to prevent late payments and ensure a smooth and consistent cash flow.
So, credit management is a broader term that includes collections and A/R management. Credit management and A/R management are proactive and preventive (as in, they help you prevent late payments or credit defaults), while collections are reactive and corrective.
Three Benefits of Credit Management
There are many benefits of credit management, three of which are:
1. Increasing your Profitability
Credit management helps establish your clients’ creditworthiness, lowering your credit risk and decreasing your credit losses.
You can also reduce your operational costs by automating and streamlining your credit management process. Consequently, credit management increases your profitability and return on investment.
2. Improving your Cash Flow
By preventing late payments, managing your credit risk, and reducing bad debts, credit management helps improve your business’s cash flow and liquidity.
It can also optimize your working capital by accelerating your cash inflows and delaying your cash outflows, helping you meet your short-term financial obligations and invest in your long-term growth.
Pro Tip: An alternative way to improve your cash flow management is by building a strong cash pool through a loan, which involves, among other things, building a Fundability Foundation™.

If you don’t have the correct foundation, you’ll be denied every time you request a business loan, regardless of what your credit report says. If you don’t know how to set up a Fundability Foundation for your business, a business credit professional can help.
3. Enhancing your Customer Relationships
Credit management can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty by providing them with flexible and convenient payment options and communicating with them regularly and proactively to resolve any issues and prevent conflicts.
Actions like these help build trust and rapport with your customers and encourage repeat purchases and referrals.
The Main Components of Credit Management
The credit management process consists of six main components:
1. New Client Assessment and Approval
The first step of credit management is evaluating the creditworthiness of your potential customers before granting them credit. You can use various methods and sources to gather information about their financial situation, such as credit reports, credit scores, bank statements, tax returns, credit history, trade references, etc.
2. Credit Policy
Your credit policy is the set of rules and guidelines that a business follows when granting credit to customers and managing credit risk.
A credit policy defines the criteria for granting credit, the terms and conditions of credit, the credit limits and payment terms, the collection procedures, and the monitoring and control mechanisms.
3. Credit Monitoring
Besides keeping an eye on your clients’ credit reports, an essential part of credit management is tracking and monitoring the performance and behavior of customers who have been granted credit.
Credit monitoring can involve reviewing the customer’s payment history, outstanding balances, aging reports, credit utilization, and other indicators of credit risk. Through these, credit management helps identify potential problems and take corrective actions before they become serious.
4. Credit Risk Mitigation
Credit risk mitigation refers to the process of reducing the exposure and impact of credit risk on your business.
The process can involve diversifying the customer base, requiring advance payments or deposits, obtaining guarantees or collateral, using factoring or invoice discounting services, or purchasing trade credit insurance.
5. Credit Collection
As mentioned above, this is the process of recovering the money owed by customers who haven’t paid their invoices on time or in full.
Credit collection can involve sending reminders, making phone calls, negotiating payment plans, offering discounts or incentives, imposing penalties or interest charges, or taking legal action.
6. Credit Extensions for Existing Customers
A critical part of credit management is monitoring and managing the credit exposure of your existing customers. Doing so allows you to assess whether you can update their credit limits or extend their payment terms if they ever face any financial difficulties or emergencies.
In the realm of credit management, understanding your client’s full financial picture is paramount. Leveraging tools that provide customer 360 insights can grant credit managers a comprehensive view of a client’s financial footprint.
This level of detail, combined with predictive analytics, can inform better credit decisions, risk assessments, and client relationship management.
Future Trends of Credit Management
Credit management is a dynamic and evolving field that’s influenced by various factors, such as customer preferences, market conditions, technological innovations, and more. Here are some of the future trends that’ll shape the credit management industry in the coming years:
1. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the technology that enables machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making. The widespread use of AI is the biggest trend in credit management for the foreseeable future.
Some of the benefits this technology brings to the table are:
- Automation and personalization of decisions across customers’ lifecycles.
- Setting payment terms and conditions using dynamic pricing.
- Enhanced detection of early warning signals of defaults.
- Improved accuracy and speed of probability of default (PD) calculations.
AI can also help credit managers collect their debts using chatbots, voice assistants, and other solutions. Benefits like these improve credit management significantly, in one case, doubling approval rates while reducing credit losses by as much as 20%.
2. Big Data
Big data refers to the large and complex sets of data generated from various sources and formats at high speed and volume. Big data can help credit managers improve their processes by providing them with more information and insights about their customers and markets.
Key data points include traditional financial data from credit bureaus, credit card companies, and other financial institutions, as well as demographic data, social media usage patterns, and much more.

The use of big data in the financial industry has been steadily increasing throughout the years. The financial sector plans to increase its budgets in big data analytics in the next three years, so this is a trend to look out for.
As data increases, so does the need to protect that data. The potential consequences of breaches, which can lead to significant financial losses and loss of trust, support the importance of data security.
Solutions such as AWS s3 Backup ensure a secure repository for this invaluable data and provide security against unexpected circumstances, data corruption, or malicious threats. In an age when data drives decision-making, having a robust backup system isn’t only a best practice but a necessity for the future of credit management.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistical methods and machine learning techniques to analyze historical and current data and make predictions about future outcomes and events.
This technology can help credit managers optimize their customer credit management process by providing them with forecasts, scenarios, simulations, and more. By doing so, they help credit managers test the impact of different credit policies and strategies on their business performance using what-if credit analysis and optimization tools.
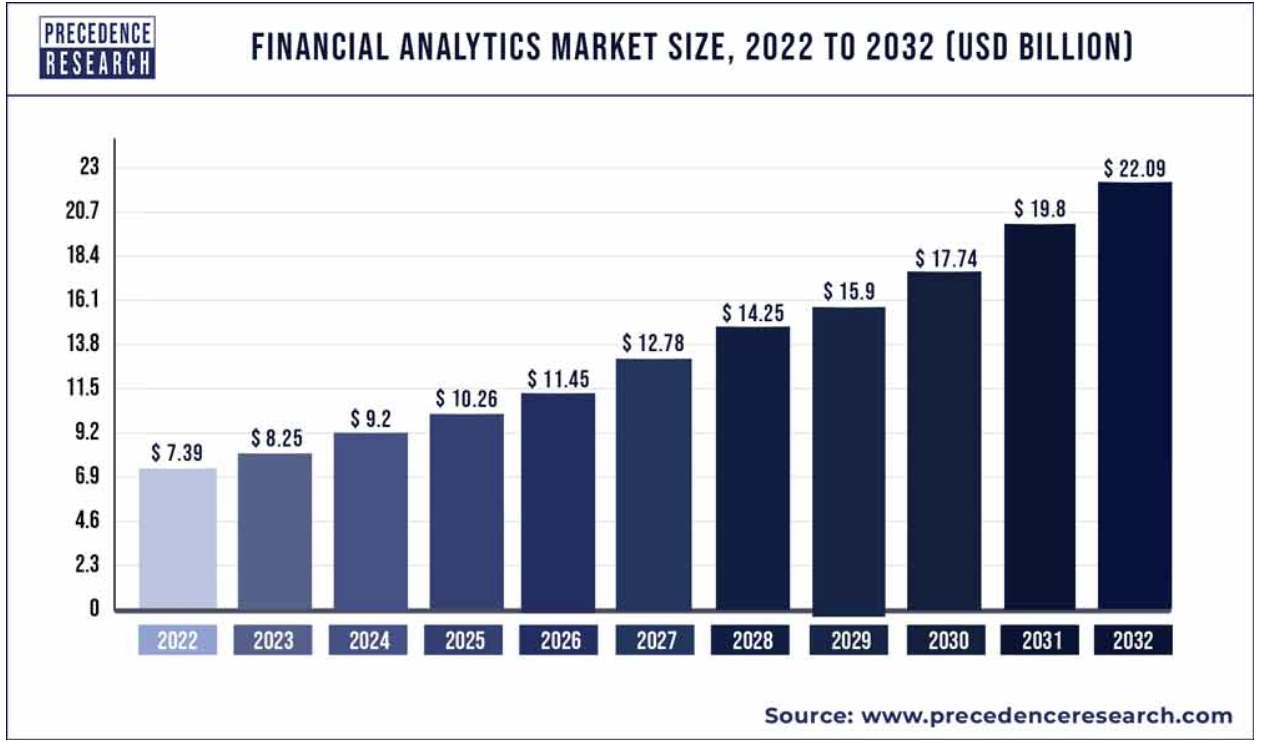
A recent market survey on using predictive analytics performed on 415 consumer lending organizations in the US revealed that 66% of organizations expect that predictive analytics models will shape the industry in the next five years. In fact, the financial analytics market is expected to grow to over $22 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 11.57%.
With predictive analytics software at the forefront, organizations can now harness the vast sea of data available to them, extracting valuable insights that were once elusive. By analyzing historical financial behaviors, market trends, and even macroeconomic indicators, this software empowers credit managers to make more informed decisions.
As we peer into the horizon of credit management, it’s evident that the adoption of predictive analytics isn’t just an option — it’s the compass guiding us toward a more precise, data-driven, and proactive approach to credit risk management.
4. A Greater Focus on Gen Z
Gen Zs are the digital natives who grew up with the internet, social media, and smartphones. They’re also future customers and employees of the credit management industry.
Gen Z has different expectations and preferences for credit management than previous generations. They value convenience, speed, transparency, personalization, and social responsibility and prefer to use digital platforms and channels to access and manage their credit accounts.
According to Bank of America, two-thirds (66%) of Gen Z are “actively saving for financial goals,” which is an important trend to follow if you’re in credit management. Credit managers need to adapt their credit management process to meet the needs and demands of Gen Z by offering them innovative and customized solutions that leverage technology and data.
5. Reskilling or Upskilling Staff for Better Data Skills
The growth of AI, big data, and data analytics we discussed above have made data skills more valuable than ever in the credit management industry. Credit managers will need to reskill or upskill their staff for better data skills by providing them with training, education, and development opportunities.
For example, credit managers can offer their staff courses or workshops on topics such as data literacy, data analysis, data visualization, data storytelling, etc.
A Shifting Future for Credit Management
The future landscape of credit management is heading for a transformative shift, thanks to the convergence of AI, big data, and cutting-edge predictive analytics.
This powerful trio, in combination with Gen Z’s technology-driven expectations and preferences, is poised to revolutionize the way businesses assess and mitigate credit risks.
If you don’t know how to set up a Fundability Foundation for your business, a business credit professional can help.


